Understanding can you have two health insurance plans is important for many Americans who receive coverage from more than one source. Some people get an employer-sponsored plan while also staying on a parent’s or spouse’s policy. Others may qualify for government programs like Medicaid or Medicare while holding private insurance.
This situation is known as dual health insurance coverage, and for many families, it helps reduce medical costs and provides extra financial protection. However, managing two plans can also be confusing because primary and secondary insurance rules decide how payments work. Knowing coordination of benefits (COB) helps you avoid claim issues and understand what each plan will cover.
What Does It Mean to Have Two Health Insurance Plans
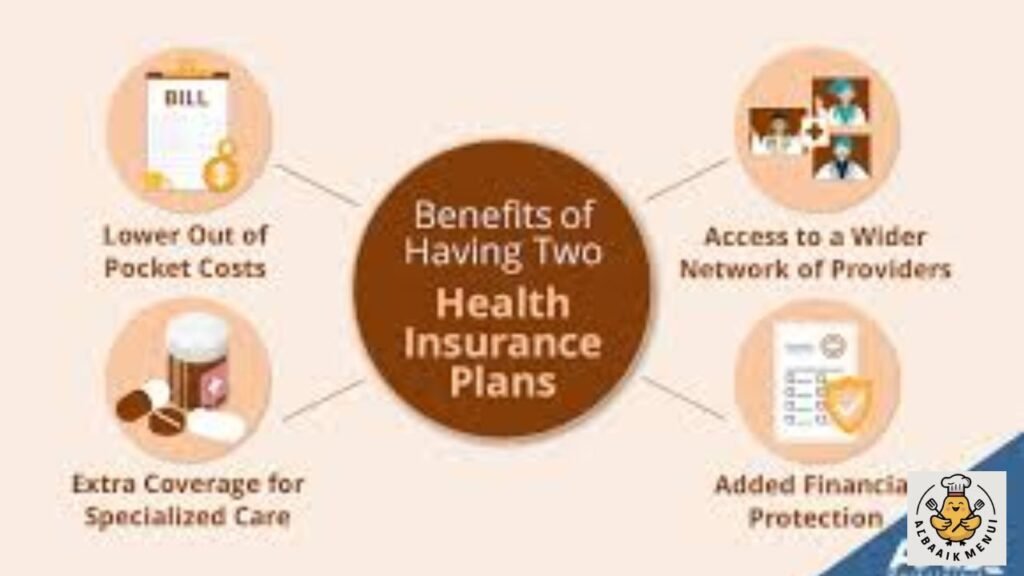
Having two policies means you are covered by a primary plan and a secondary health plan, and both contribute to your medical bills through something insurers call dual health insurance coverage.
This setup creates a layered shield that helps manage treatment costs, but it never pays more than your total bill. Many Americans rely on this structure when balancing care between an employer-sponsored health plan and a spouse’s coverage or when supporting a child through dependent insurance coverage.
Dual coverage rises in situations like a university medical plan, a parent policy, or government-backed benefits where Medicaid is usually secondary. These combinations follow strict coordination of benefits (COB) rules that protect insurance companies from duplicate payments.
When explained in simple terms, these rules make sure the primary plan covers first, and then the second fills remaining gaps.
How Dual Health Insurance Coverage Works
Every claim follows an order. Under federal guidelines, primary and secondary insurance are assigned by law, not personal choice. The primary insurer processes a claim first, pays its part, and then sends an explanation of benefits (EOB). Only after that secondary insurance kicks in after primary, filling whatever is left based on its own rules and coverage limits and cost-sharing structure.
Think of it like a financial ladder. The first plan climbs until it reaches its limits. After that, the second begins climbing. This makes insurance claims processing slower but usually more complete. It can lower your out-of-pocket medical expenses, especially if the second plan offers stronger healthcare cost coverage for services that the primary excludes.
Primary vs Secondary Health Insurance: Key Differences
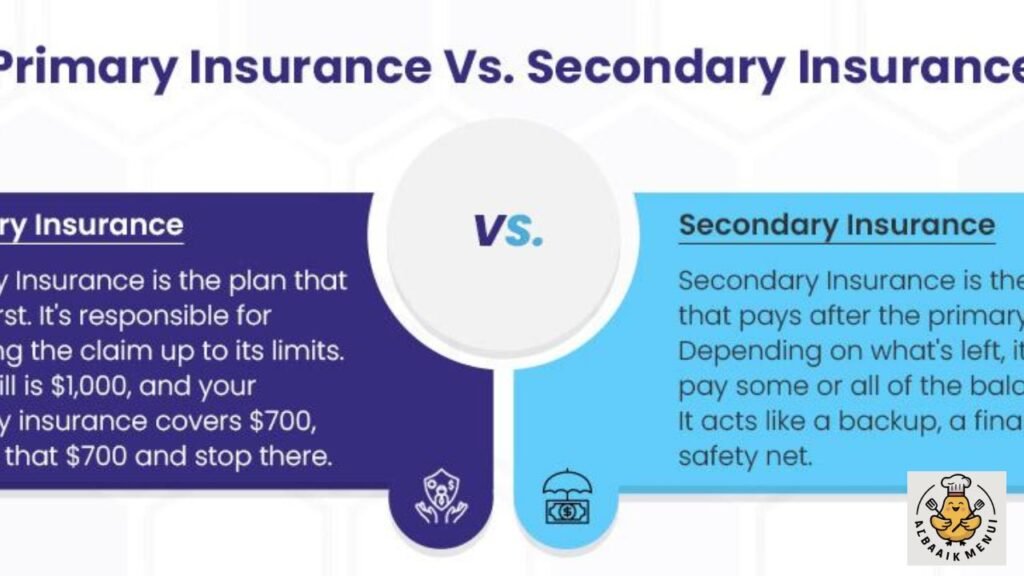
Your primary coverage always pays before anything else, even when you hold the same level of benefits through an employer or spouse. This is why the primary plan covers first in every case. The secondary only pays after reviewing the EOB and confirming unpaid balances. It never overlaps beyond allowed charges, and that rule protects both you and insurers from overbilling.
The secondary plan does not guarantee full coverage. It simply follows a second layer of protection. If both policies have deductibles and copays, then you may still pay those costs yourself. That is one of the pros and cons of having two insurance plans because, while protection increases, your monthly premiums can increase, too.
Rules That Determine Which Insurance Is Primary

The USA uses legal guidelines to determine which insurance is primary. When you have job-based coverage and your spouse has one, the parents’ plan vs employer plan rule places your employer’s plan first. When a child has two policies, the birthday rule for dependents assigns priority to the parent whose birthday arrives earlier in the year.
In homes with shared custody, the divorced parents insurance coordination rule makes the custodial parent’s policy primary. In government programs, Medicaid is usually secondary, while Medicare and COBRA coordination rules make Medicare primary for retirees and COBRA secondary for those continuing employer coverage temporarily. When timing matters, the length of coverage rule states that whichever plan you held longer becomes primary.
Common Scenarios Where Two Health Insurance Plans Apply

Many Americans experience dual coverage when a student under 26 uses a university medical plan while remaining on a parent’s policy. Others rely on a spouse employer plan plus personal plan to increase benefits. These households often prefer layered protection because one plan fills gaps in the other.
Dual coverage is also common when two working parents provide insurance for a child, when someone is transitioning between jobs, or when chronic health needs require more support. Senior citizens often experience coordination between employer coverage and Medicare, creating one of the most complex examples of medical billing coordination.
Reasons Why People Choose Dual Health Insurance Coverage

Dual coverage often provides peace of mind. When bills pile up or major surgery approaches, having two layers of protection limits stress. Some families rely on it to manage unpredictable costs, while others use it to maintain care when switching jobs or moving states. When kids are involved, students under age 26 dual coverage becomes a wise financial choice.
Another reason relates to chronic illness. If one policy excludes certain medications, the second might cover them. Dual protection also works well for households balancing employer benefits with Medicaid, where Medicaid secondary payer rules help families reduce leftover medical bills.
Pros and Cons of Having Two Health Insurance Policies

Having two policies increases protection against expensive surprises and often reduces long-term medical burden. This can be helpful for families with multiple health needs or people who want stronger hospital coverage. Dual benefits allow one plan to fill in gaps in the other, improving healthcare cost coverage.
Still, there are drawbacks. Some families face extra out-of-pocket costs because each plan may charge its own cost-sharing fees. You also deal with complex claim processing, especially when the secondary insurer requires proof of payment before releasing funds. These situations make many people ask, is dual insurance worth it?
Can Dual Insurance Help You Save Money

Dual coverage can reduce costs when you face ongoing treatments, major procedures, or repeated medication needs. The secondary plan fills unpaid balances left behind by the primary and limits what you pay from your wallet. It becomes especially useful when dealing with specialist visits or long hospital stays.
Savings increase when employers offer a health reimbursement arrangement (HRA), where employees receive health insurance reimbursements via HRA to cover extra charges. This includes individual coverage HRA (ICHRA), qualified small employer HRA (QSEHRA), and group coverage HRA (GCHRA).
These reimbursements apply to minimum essential coverage (MEC) plans and support families by reducing out-of-pocket medical expenses.
How Claims Are Processed With Two Health Insurance Plans
The claim process requires patience. First, the primary insurer reviews your service and pays its share. You receive an explanation of benefits (EOB) showing what was covered and what remains. Then the secondary insurer evaluates the leftover balance and pays based on its limits. This may take time because insurance claims processing requires proper documentation.
Many people face delays when paperwork is missing or when policies disagree about which plan should pay first. These delays highlight why managing two health insurance policies requires careful recordkeeping. Once the process is understood, dual coverage becomes easier to control.
Final Thoughts: Is Having Two Health Insurance Plans Worth It
So Can you have two health insurance plans? Yes, and millions of Americans rely on dual coverage for stronger financial protection. It works best for families who want layered support, individuals with complex medical needs, and students or employees balancing multiple policies. With the right coordination, two plans can significantly reduce medical stress.
Understanding your COB rules, payment order, and policy timing is key to avoiding confusion. When done right, dual coverage becomes a smart way to stretch benefits and shield your wallet. For many households across the United States, it remains one of the most valuable strategies for long-term health security.
FAQS
Is it worth it to have two health insurance plans
Sometimes yes, especially if the secondary plan helps reduce your out-of-pocket costs, but it can also increase your monthly premiums.
How does insurance work if you have two
Your primary plan pays first, and your secondary plan covers remaining costs based on coordination of benefits rules.
Can you legally have two health insurance plans
Yes, dual health insurance is legal in the USA as long as both plans allow coordination of benefits.
Is double insurance allowed
Yes, it is allowed, and many people have it through employers, parents, spouses, or government programs.
What happens if you accidentally have two health insurance plans
Nothing harmful; the insurers will simply decide which one is primary, but you may pay extra premiums if you don’t cancel one.




